R2. Kinematics
Table of Contents
1 Info
The assignment presents properties of serial robot kinematics and Denavit-Hartenberg notation.
The points marked with (*) are optional (not obligatory).
2 Preparation
Before the classes recall from the lecture definitions of robot kinematics and Denavit-Hartenberg notations. Prepare the formulas to calculate the kinematics from D-H parameters. Consider which functions from the toolbox will be needed to solve the current tasks.
3 Tasks
Task 0: Complete unfinished tasks from the previous assignment
Task 1: Kinematics of a 3R robot
- According to Denevit-Hartenberg algorithm define homogenous transformations for an RRR robot (A01, A12, A23):
Assume the link lengths are, respectively, 2, 1, and 1. When the robot joint angles are equal to 0 the robot second and third arms are placed horizontaly.
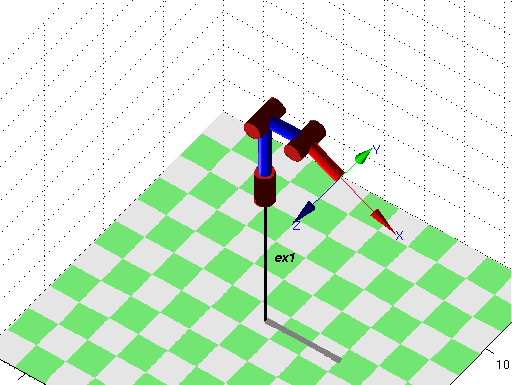
- For selected joint angles plot coordinate systems associated with each joint.
- Assume q1=q2=q3=0. What are expected positions and orientations of coordinate systems? What is expected translation vector in robot kinematics? What is expected rotation?
- Calculate the kinematics for the joint values from the previous item. Is the result the same as expected?
- For the same joint angles calculate Euler angles from kinematics transformation. Check the result with the expected value.
- To report:
- Write homogenous transformations for each joint and kinematics for the joint angles q1=0, q2=π/4, q3=-π/6. Include Matlab code used to obtain these matrices.
- Find the joint angles for which the translation vector of the kinematics is [0,1,3].
Task 2: SerialLink manipulator
- Define an RT robot using toolbox functions.
Verify its D-H parameters.
>> import ETS3.* >> rob=SerialLink([Revolute('d',1,'alpha',pi/4) Prismatic('a',1)]) >> rob.name='RT' - Calculate kinematics for given joint angle and translation and
plot the result
>> rob.fkine([pi/4 1])
- Use SerialLink toolbox function to define the robot from task 1.
- Calculate its kinematics, plot it, compare the results with task 1 results.
- To report:
- Include code.
Task 3*: Kinematics of industrial robots
- Examine any of the toolbox predefined industrial robot models ('models' command to list them, toolbox script given in parentheses at the end of each line to read in the model, e.g. 'mdl_KR5').
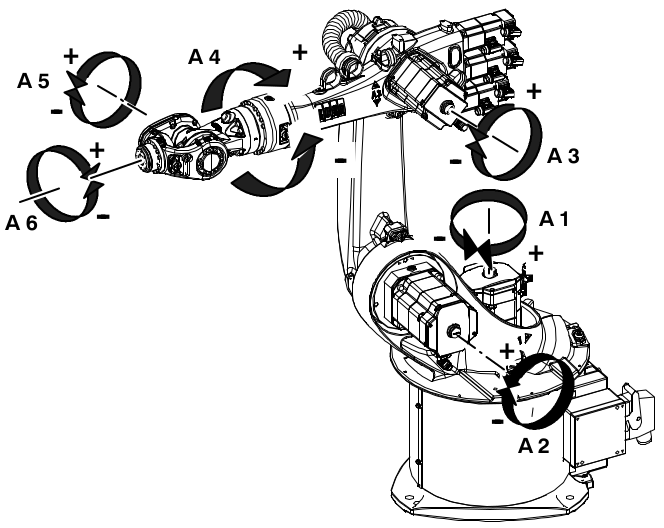
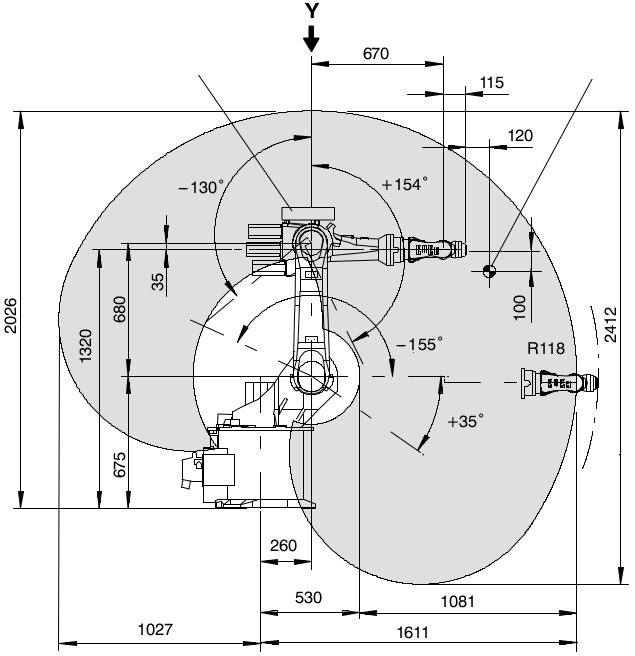
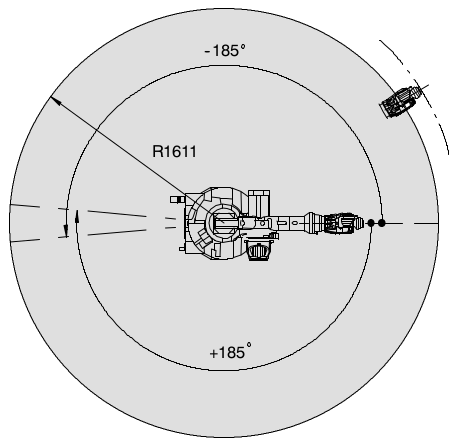
- Find D-H parameters for the Kuka KR16 industrial robot presented below.
- Calculate kinematics for selected joint angle values.
- To report:
- Include a matrix of D-H parameters
- Include a vector of joint angles and kinematic matrix calculated for it.
4 Summary
- The report should include the result of the tasks and answers to the questions.
- Please do not forget to indicate the author of the report!
- The report in PDF format should be submitted before the beginning of next classes using a method defined by the instructor.